Representatives from Satelles and the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) submitted a jointly written paper at the most recent Institute of Navigation (ION) Precise Time and Time Interval Systems and Applications (PTTI) meeting, an event held concurrently with ION’s International Technical Meeting.
The paper, entitled “Measuring the Timing Accuracy of Satellite Time and Location (STL) Receivers,” was co-developed by time experts at Satelles and NIST. The underlying research demonstrated that a calibrated STL receiver can achieve an average time offset better than 18 ns with respect to UTC(NIST) with a peak-to-peak variation of 325 ns for a typical OCXO receiver and better than 80 ns with a rubidium-based receiver.
The following chart visualizes the comparison of STL to UTC(NIST) for a 30-day period. The blue line depicts the time offset between UTC(NIST) and an STL receiver with an OCXO oscillator, and the red line represents the same measurement for an STL receiver with a rubidium oscillator.
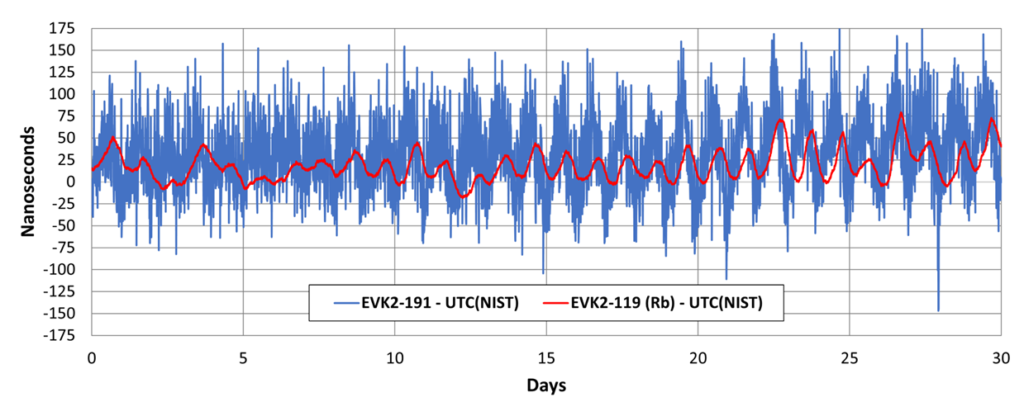
In addition, strong repeatability was achieved between calibrations made at the Satelles laboratory and those conducted at NIST, demonstrating that even an uncalibrated STL receiver should easily provide sub-microsecond accuracy and that accuracies below 100 ns are achievable with delay calibration.
The findings from the paper are just the latest that point to STL as a reliable source of timing that is not only highly consistent with Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) but also one that has broad applicability across a range of timing synchronization applications that safeguard the operations of critical infrastructure (e.g., 5G, data centers, financial services, and other sectors).
NOTE: Read more about other collaborations between Satelles and NIST.
The paper co-written with NIST was just one aspect of our involvement at ION ITM/PTTI. Some other relevant Satelles and STL updates from the conference:
- Researchers from the GPS & Vehicle Dynamics Laboratory at Auburn University presented an STL-focused paper with the title “Precision Timing with LEO Satellite Time and Location Signals.” Among the paper’s conclusions was that STL can be utilized as a highly stable backup or complement to GNSS UTC and time interval synchronization.
- Sync-n-Scale provided a video presentation in one of the PTTI tracks. Entitled “Detecting Manipulated Spaceborne Positioning and Timing Using Ground-Based Commercial-Off-The-Shelf Assets and Services,” the video showcased a proof-of-concept data center solution that pairs GPS and STL inside a secure system to ensure maximum PNT resilience.
- Dr. Michael O’Connor, CEO of Satelles, was the co-chair of an ITM session called “Alternatives, Backups, and Complements to GNSS.” Presentations in this session were delivered by academic researchers, government officials, and commercial entities from around the world.



